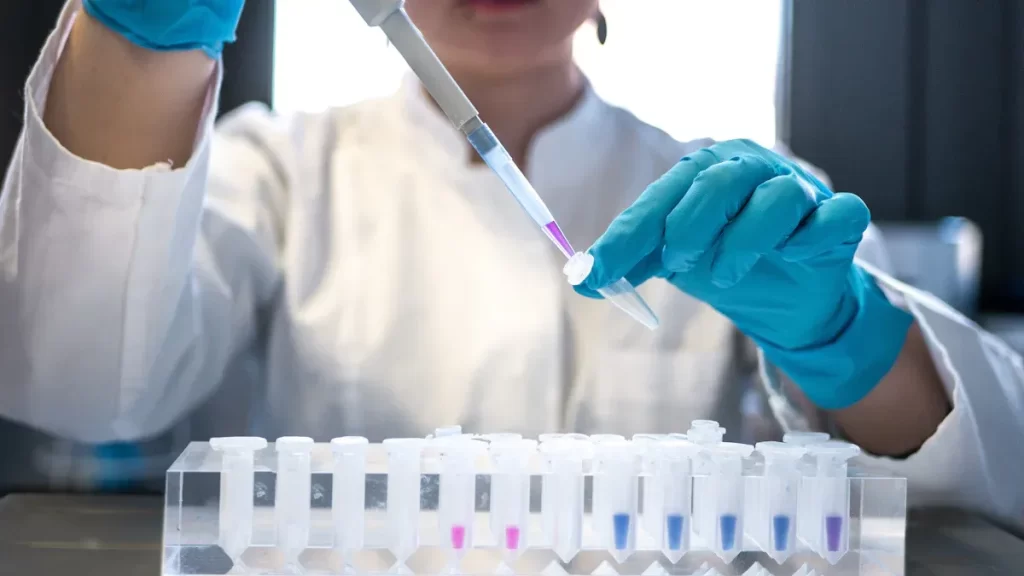
Bradford protein estimation ensures accurate quantification for Western blot analysis. Follow each step to avoid errors and achieve reliable protein results.
Category Archives: Antibody knowledge
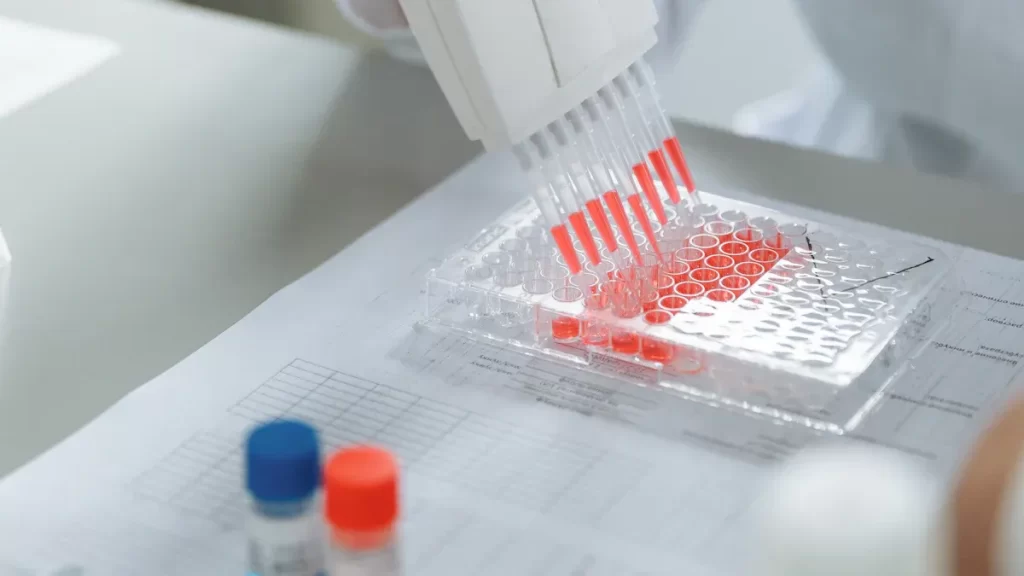
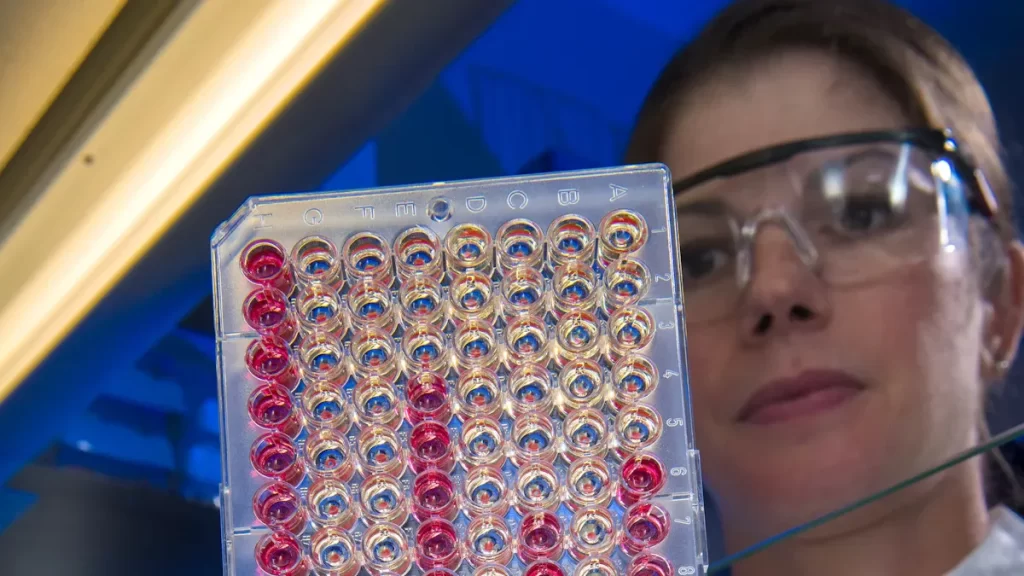
ELISA immunoassay kits simplify testing by reducing manual steps, minimizing errors, and delivering fast, reliable results for efficient lab workflows.
Compare ELISA and immunoprecipitation for ab rubella igg testing to choose the most accurate method for reliable rubella immunity detection.
Compare strep test kit and ELISA immunoassay for streptococcal diagnosis. See which method offers faster, accurate results for clinical decision-making.
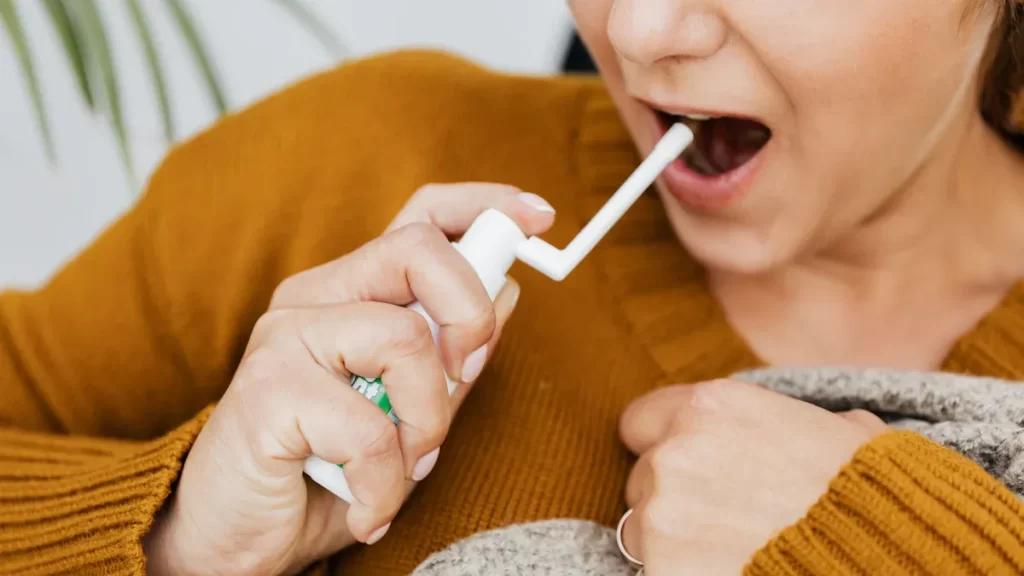
Rubella virus IgG Ab testing confirms immunity and guides pregnancy care, helping prevent congenital rubella syndrome and related complications.
Rubella IgG antibody testing solutions provide accurate immunity assessment and reliable diagnostics for clinical and research applications.
The reagent in total protein test ensures accurate protein quantification by using coomassie dye, acid, and solvent for reliable Bradford assay results.
Lab 34 peptides and proteins reveal how structure, rare amino acids, and lab techniques impact stability, folding, and medical applications.
Oligonucleotide ligation assay advances enable rapid, sensitive detection of HIV resistance and genetic mutations for improved disease diagnostics.
Flow Cytometry PrincipleFlow cytometry has a multitude of applications in science, but the basic principle of operation is fairly simple: Cells (or other particles) pass in single file in front of a laser which allows them to be detected, counted, and sorted. These particles are fluorescently labelled, and the laser excites the fluorescent tags which […]
- 1
- 2