News & Events
Breaking Down DNA DS Antibody Testing for Better Health Decisions

Have you ever wondered why your symptoms, like joint pain, fatigue, or skin rashes, keep coming back? You might have heard about lupus or even systemic lupus erythematosus, which can cause these ongoing symptoms. The dna ds antibody plays a key role in lupus. Doctors use the anti-double stranded dna test as a major diagnostic tool. This test helps with early diagnosis and guides treatment decisions.
- About 70% to 98% of lupus patients test positive for this antibody.
- Early testing improves diagnostic accuracy, which can prevent organ damage.
| Misconception | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Anti-ssDNA antibodies are common in other rheumatic diseases | Only 10–15% of people with rheumatoid arthritis have them, not most. |
| Clinical utility of anti-ssDNA testing | It helps diagnose lupus when anti-dsDNA is not found. |
| Specificity of anti-ssDNA tests | Sensitivity for lupus is nearly 100%, with about 85% specificity. |
You can feel confident discussing your symptoms and test results with your healthcare provider.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the dna ds antibody is crucial for diagnosing lupus. Over 98% of lupus patients test positive for this antibody, making it a key marker.
- Early testing for anti-double stranded DNA antibodies can improve diagnostic accuracy and help prevent organ damage.
- Different laboratory methods, like ELISA and CLIFT, have varying sensitivity and specificity. Knowing which test your doctor uses can help you understand your results better.
- A positive anti-double stranded DNA test suggests active lupus, especially if you have symptoms. Regular monitoring can help manage flare-ups effectively.
- Discuss your test results with your doctor to make informed health decisions. Understanding your results empowers you to advocate for your health.
DNA DS Antibody Basics

What Is a DNA DS Antibody?
You may wonder what a dna ds antibody actually is. This special antibody targets double-stranded DNA, which is the genetic material found in your cells. Your immune system sometimes makes these antibodies by mistake. When this happens, your body starts to attack its own DNA. This process is common in autoimmune diseases.
- dna ds antibody is a type of autoantibody that binds to double-stranded DNA.
- Your immune system produces these antibodies, especially if you have lupus.
- The anti-dsdna antibody test can detect these antibodies in your blood.
In the general population, only about 7.2% of people have dna ds antibody. If you have lupus, the number jumps much higher. Over 98% of people with lupus test positive for this marker. This makes the dna ds antibody a strong clue for lupus diagnosis.
Role in Lupus
Lupus is a disease where your immune system attacks healthy tissues. The dna ds antibody plays a big part in this process. When these antibodies bind to your DNA, they form immune complexes. These complexes can travel in your blood and settle in organs like your kidneys. This can cause inflammation and damage.
- dna ds antibody helps doctors confirm a lupus diagnosis.
- High levels of this antibody often mean lupus is active.
- The anti-dsdna antibody test is a key tool for tracking lupus activity.
Doctors use the dna ds antibody as a diagnostic marker. They also use it to monitor how lupus changes over time. Studies show that higher levels of this antibody link to more severe lupus symptoms. The chart below shows how different testing methods relate to lupus activity and kidney involvement.
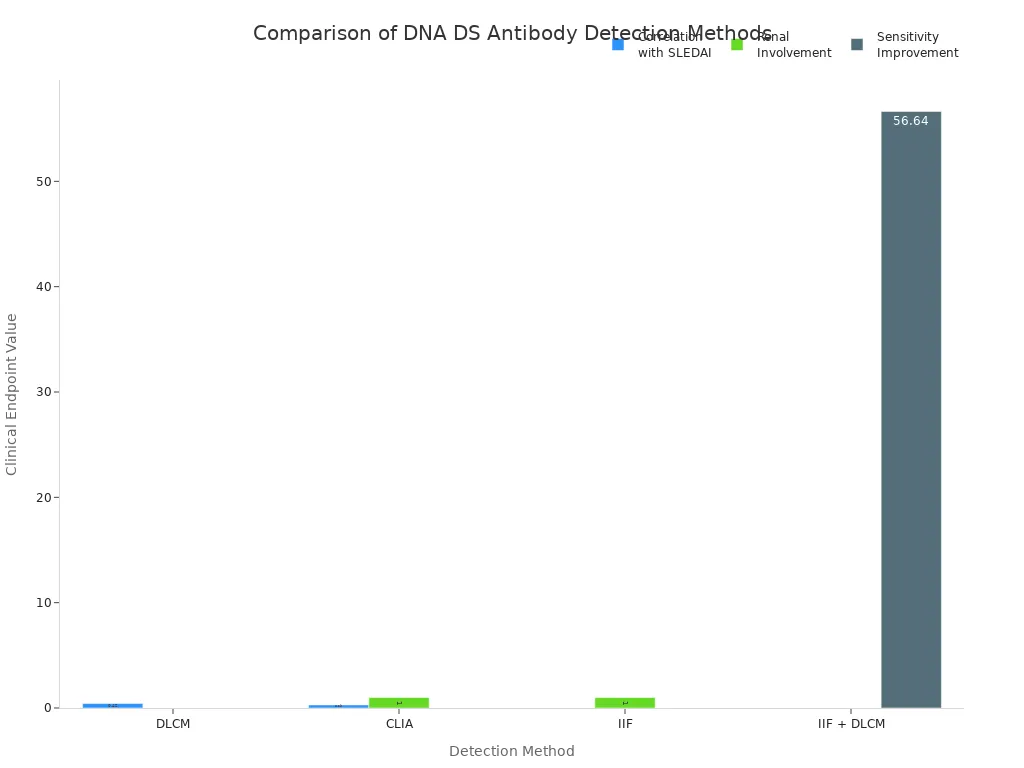
You can see why understanding your dna ds antibody levels is important. This knowledge helps you and your doctor make better health decisions and manage lupus more effectively.
Anti-Double Stranded DNA Test Methods
ELISA, CLIFT, and Farr Assay
When you visit a laboratory for lupus testing, you may hear about different ways to check for anti-double stranded DNA antibodies. The three main methods are ELISA, CLIFT, and the Farr assay. Each method helps your doctor understand how your immune system is working.
Here is a table that compares these methods:
| Method | Sensitivity | Specificity | Clinical Applicability |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | High | Low | Preferred for monitoring disease activity |
| CLIFT | Low | High | Not suitable for screening, subjective interpretation |
| Farr | High | High | Rarely used clinically due to radioactive materials |
- ELISA stands for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. This laboratory test is common for detecting anti-dsdna antibodies. Doctors often use ELISA to monitor lupus activity.
- CLIFT means Crithidia Luciliae Immunofluorescence Test. This laboratory test has high specificity but lower sensitivity. You may not get this test for screening because it can miss some cases.
- The Farr assay is another laboratory method. It has both high sensitivity and high specificity. Most laboratories do not use it now because it involves radioactive materials.
You may also have an antinuclear antibody test before these specific tests. This helps doctors decide which laboratory method to use next.
Test Accuracy
You want your lupus diagnosis to be as accurate as possible. The accuracy of each laboratory test depends on sensitivity and specificity. Sensitivity shows how well the test finds people with lupus. Specificity shows how well the test avoids false positives.
- ELISA sensitivity ranges from 55% to 88%. Specificity ranges from 84% to 98%.
- CLIFT has a positivity rate of 68% and specificity of 84%.
- The Farr assay is very accurate but not used often in most laboratories.
The choice of laboratory test can affect your results. Some tests may give false positives, especially if you have other autoimmune diseases or infections. Even healthy people can sometimes test positive. Doctors use the antinuclear antibody test along with these methods to improve accuracy.
Tip: Always ask your doctor which laboratory test they use for lupus. This helps you understand your results better.
The laboratory method for detecting anti-dsdna antibodies can change your diagnosis and treatment plan. Knowing how each test works helps you make better health decisions.
Interpreting Test Results
Normal, Equivocal, Positive Values
When you receive your anti-double stranded DNA test results, you might see numbers and terms like “negative,” “equivocal,” or “positive.” These values help you and your doctor understand your risk for lupus and lupus nephritis. Different labs may use slightly different reference ranges, but most follow similar guidelines.
Here is a table showing common reference ranges for anti-double stranded DNA test results:
| Result Type | Reference Range (IU/mL) |
|---|---|
| Negative | < 27 |
| Borderline Positive | 27 – 35 |
| Positive | ≥ 36 |
Some labs may use other cutoffs, such as:
| Result Type | Reference Range (IU/mL) |
|---|---|
| Normal | < 10 |
| Equivocal | 10 – 15 |
| Positive | > 15 |
You should always check which range your lab uses. If your result falls in the “negative” or “normal” range, you likely do not have active lupus. An “equivocal” or “borderline” result means the test is not clear. Your doctor may repeat the test or look at other signs. A “positive” result means your immune system is making antibodies against your own DNA. This is a strong clue for lupus, especially if you have symptoms.
Tip: Always ask your doctor to explain your test results in the context of your symptoms and other lab findings.
What Results Mean for Lupus
Your anti-double stranded DNA test results play a big role in diagnosing and managing lupus. A positive result suggests that your immune system is very active. This is especially important if you have signs of lupus nephritis, which affects your kidneys.
- A positive test result for this antibody is highly suggestive of lupus when you also have symptoms.
- Weak-positive results do not always mean you have lupus. Your doctor will look at your whole health picture.
- Negative results do not rule out lupus. Some people with lupus, especially early in the disease, may have negative results.
Your doctor uses these results to track lupus activity. When your anti-double stranded DNA levels rise, it often means a lupus flare is coming. This is especially true for lupus nephritis. Doctors also check other markers, like complement proteins (C3 and C4), to get a full picture of your disease.
Here is a table that explains what your results might mean:
| Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive dsDNA IgG antibodies | Suggest lupus, especially if you have symptoms and signs of lupus nephritis. |
| Weak-positive results | May not mean lupus. Your doctor will consider other factors. |
| Negative results | Do not rule out lupus. You may still need more tests. |
You may notice that your doctor orders this test often. That is because changes in your anti-double stranded DNA levels can show if your lupus is getting worse or better. High levels often mean your lupus is active. This is very important for lupus nephritis, where kidney damage can happen quickly.
- The test is essential for monitoring lupus flare-ups.
- It is especially important for checking lupus nephritis.
- Rising anti-double stranded DNA levels often mean a flare is coming.
- Doctors use this test along with complement levels to predict and manage flares.
If you have a positive result, your doctor may want to check your anti-double stranded DNA levels and complement proteins every few months. If your lupus is quiet, you may only need testing every 6 to 12 months. If you have signs of lupus nephritis or your results stay high, you may need testing every 3 to 4 months.
Note: Regular testing helps your doctor catch lupus nephritis early and protect your kidneys.
You can use your test results to make better health decisions. If your levels go up, you may need to adjust your treatment. If your results stay low, your lupus may be under control. Always talk to your doctor about what your results mean for you.
Lupus Lab Tests and Health Decisions
When to Get Tested
You might wonder when you should ask your doctor about lupus lab tests. Doctors often order an anti-double stranded DNA test if you have a positive antinuclear antibody test and symptoms that suggest lupus. These symptoms can include:
- Persistent fatigue
- Joint pain
- Skin rashes, especially a butterfly-shaped rash
- Unexplained fever
| Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | You may feel tired even after resting. |
| Joint pain | Your joints might hurt or swell. |
| Skin rashes | Rashes can appear, often on your face. |
| Unexplained fever | You may have a fever without a clear reason. |
Doctors also use lupus lab tests to monitor your disease if you already have a diagnosis. If your symptoms get worse or you have a flare, your doctor may repeat the test. Lupus lab tests help your doctor see if your antibody levels are changing. This can help predict when a flare might happen.
Tip: If you notice new symptoms or your current symptoms get worse, talk to your doctor about repeating lupus lab tests.
Impact on Treatment Choices
Your test results play a big role in your treatment plan. When your anti-double stranded DNA antibody levels rise, your doctor may change your medicine or increase your dose. Some medicines, like baricitinib, can lower antibody levels and help control lupus. Doctors use your results to decide if you need stronger treatment, especially if you have lupus nephritis.
| Evidence Description | Findings |
|---|---|
| Baricitinib reduces anti-dsDNA levels | This medicine can lower antibody levels in people with high results. |
| Anti-dsDNA as a disease activity marker | Rising levels often mean a lupus flare is coming. |
| Anti-dsDNA in lupus nephritis (LN) | High levels are common in lupus nephritis and show more severe disease. |
Doctors may repeat lupus lab tests every few months to track your results. If your results stay high, you may need more frequent testing. Changes in your results can help your doctor catch flares early and protect your organs. High antibody levels can appear years before kidney problems start, so regular lupus lab tests are important for long-term health.
Note: Always ask your doctor how your test results affect your treatment plan. Understanding your results helps you make better health decisions.
Understanding your DNA DS antibody test results gives you power in lupus care. You see how these results show disease activity and help you talk with your doctor about treatment. When you know what your results mean, you can spot lupus flare-ups early and work with your provider for timely care.
- These results guide your health decisions and support clear conversations with your healthcare team.
- Lab results can seem confusing, but learning about them helps you manage lupus better.
| Study Title | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Patient-reported outcome measures for systemic lupus erythematosus | Patient education improves self-management and supports better results. |
| Social determinants of health and disparities across the Patient pathway in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | Health literacy and tailored education boost treatment success. |
| Investigating Health Literacy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | Literacy-sensitive approaches improve medication use and results. |
You can use this knowledge to advocate for your health and make informed choices about lupus.
FAQ
What does a positive anti-double stranded DNA test mean?
A positive result means your immune system makes antibodies that target your own DNA. This often points to lupus, especially if you have symptoms. Your doctor will use this result with other tests to confirm a diagnosis.
Can you have lupus with a negative anti-dsDNA test?
Yes, you can. Some people with lupus do not have these antibodies, especially early in the disease. Your doctor will look at your symptoms and other lab results to help make a diagnosis.
How often should you get tested for anti-dsDNA antibodies?
Your doctor may suggest testing every 3 to 6 months if you have active lupus. If your disease is stable, you might only need testing once or twice a year. Always follow your doctor’s advice.
Do other diseases cause positive anti-dsDNA results?
Some infections or autoimmune diseases can cause a weak positive result.
However, high levels are most common in lupus.
Your doctor will check for other causes if your test is positive.

